
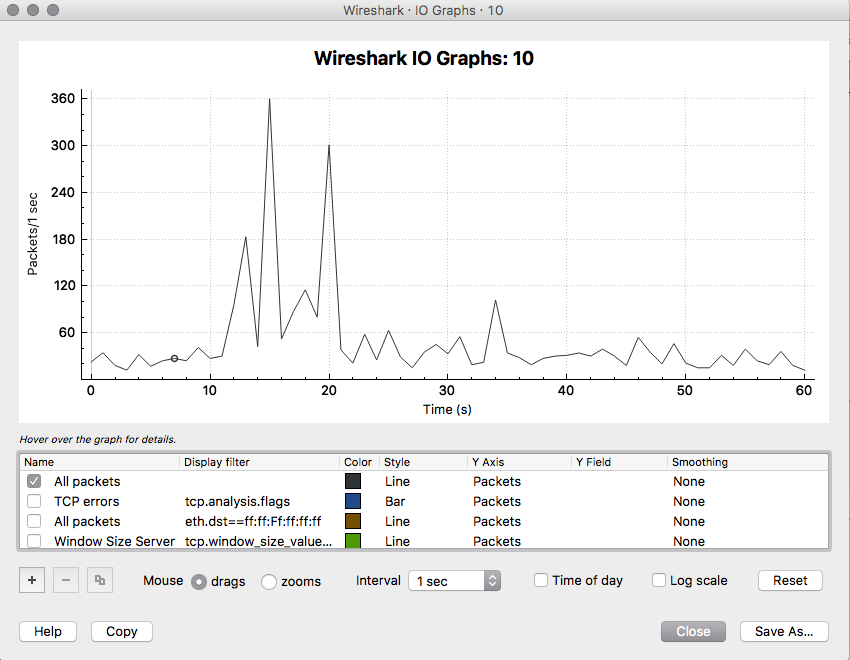
The following features are new (or have been significantly updated) since version 3.7.1:
The Windows installers now ship with Npcap 1.70. The following features are new (or have been significantly updated) since version 3.7.2:. The Windows installers now ship with Npcap 1.71. The macOS packages now ship with Qt 6.2.4 and require macOS 10.14. The following features are new (or have been significantly updated) since version 4.0.0rc1: Output can be exported to XML, PostScript®, CSV, or plain text. Coloring rules can be applied to the packet list for quick, intuitive analysis. Decryption support for many protocols, including IPsec, ISAKMP, Kerberos, SNMPv3, SSL/TLS, WEP, and WPA/WPA2. Live data can be read from Ethernet, IEEE 802.11, PPP/HDLC, ATM, Bluetooth, USB, Token Ring, Frame Relay, FDDI, and others (depending on your platfrom). Capture files compressed with gzip can be decompressed on the fly. 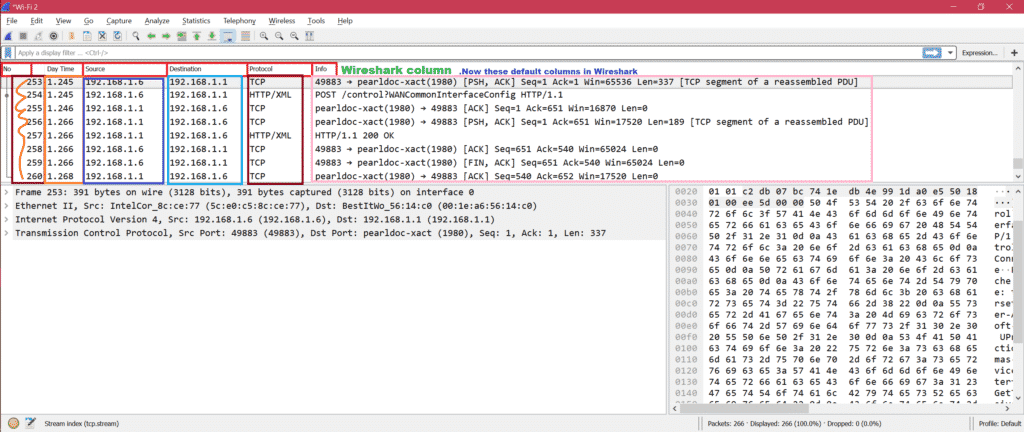 Read/write many different capture file formats. The most powerful display filters in the industry. Captured network data can be browsed via a GUI, or via the TTY-mode TShark utility. Multi-platform: Runs on Windows, Linux, OS X, Solaris, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and many others.
Read/write many different capture file formats. The most powerful display filters in the industry. Captured network data can be browsed via a GUI, or via the TTY-mode TShark utility. Multi-platform: Runs on Windows, Linux, OS X, Solaris, FreeBSD, NetBSD, and many others. 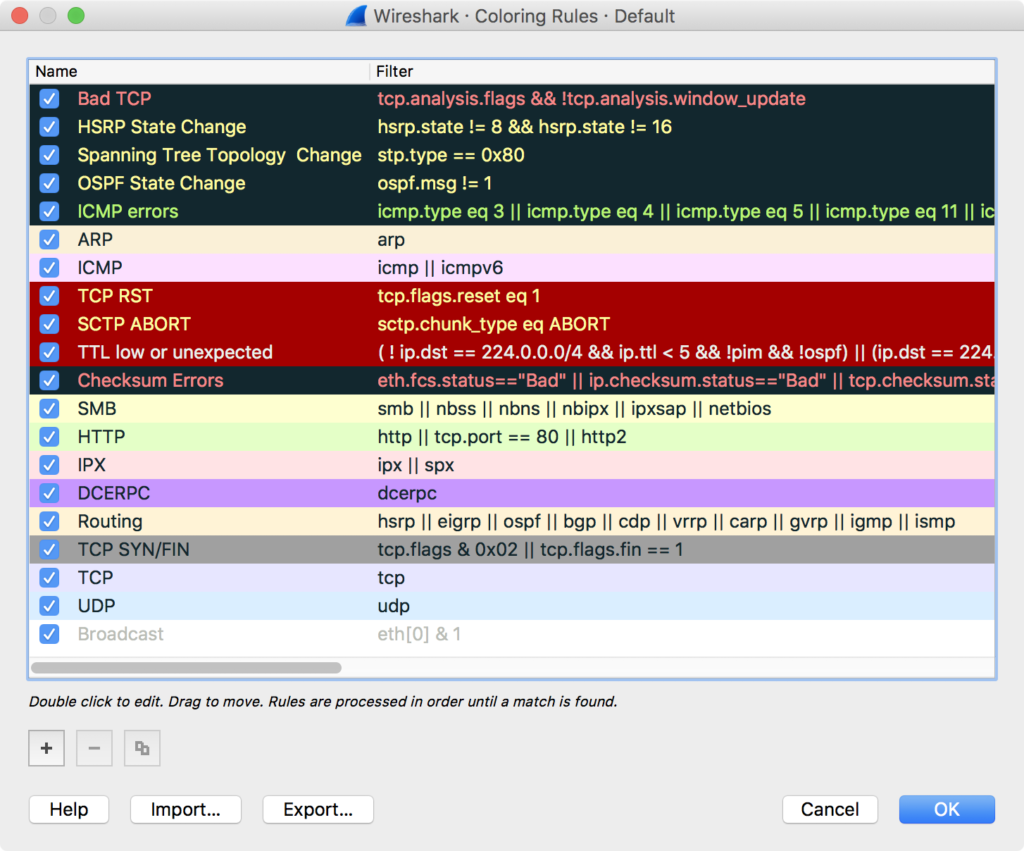 Deep inspection of hundreds of protocols, with more being added all the time. Wireshark is perhaps one of the best open source packet analyzers available today. However, with the advent of Wireshark, all that has changed. In the past, such tools were either very expensive, proprietary, or both. You could think of a network packet analyzer as a measuring device used to examine what's going on inside a network cable, just like a voltmeter is used by an electrician to examine what's going on inside an electric cable (but at a higher level, of course). A network packet analyzer will try to capture network packets and tries to display that packet data as detailed as possible.
Deep inspection of hundreds of protocols, with more being added all the time. Wireshark is perhaps one of the best open source packet analyzers available today. However, with the advent of Wireshark, all that has changed. In the past, such tools were either very expensive, proprietary, or both. You could think of a network packet analyzer as a measuring device used to examine what's going on inside a network cable, just like a voltmeter is used by an electrician to examine what's going on inside an electric cable (but at a higher level, of course). A network packet analyzer will try to capture network packets and tries to display that packet data as detailed as possible.










